8-2 使用POCO加载关联实体
问题
你想使用POCO预先加载关联实体。
解决方案
假设你有如图8-3所示的模型。

图8-3. 一个包含实体Venue、Event和Competitor的模型
实体使用POCO类,我们想预先加载关联实体(导航属性)。并使用上下文对象中的Include()方法来实现。代码清单8-4演示了使用Include()方法来实现我们的要求。
代码清单8-4. 使用Include()方法显式加载导航属性
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { RunExample(); } static void RunExample() { using (var context = new EFRecipesEntities()) { var venue = new Venue { Name = "Sports and Recreational Grounds" }; var event1 = new Event { Name = "Inter-school Soccer" }; event1.Competitors.Add(new Competitor { Name = "St. Mary's School" }); event1.Competitors.Add(new Competitor { Name = "City School" }); venue.Events.Add(event1); context.Venues.Add(venue); context.SaveChanges(); } using (var context = new EFRecipesEntities()) { foreach (var venue in context.Venues.Include("Events").Include("Events.Competitors")) { Console.WriteLine("Venue: {0}", venue.Name); foreach (var evt in venue.Events) { Console.WriteLine("\tEvent: {0}", evt.Name); Console.WriteLine("\t--- Competitors ---"); foreach (var competitor in evt.Competitors) { Console.WriteLine("\t{0}", competitor.Name); } } } } using (var context = new EFRecipesEntities()) { foreach (var venue in context.Venues) { Console.WriteLine("Venue: {0}", venue.Name); context.Entry(venue).Collection(v => v.Events).Load(); foreach (var evt in venue.Events) { Console.WriteLine("\tEvent: {0}", evt.Name); Console.WriteLine("\t--- Competitors ---"); context.Entry(evt).Collection(e => e.Competitors).Load(); foreach (var competitor in evt.Competitors) { Console.WriteLine("\t{0}", competitor.Name); } } } } Console.WriteLine("Enter input:"); string line = Console.ReadLine(); if (line == "exit") { return; }; } } public partial class Competitor { public int CompetitorId { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public int EventId { get; set; } public virtual Event Event { get; set; } } public partial class Event { public Event() { this.Competitors = new HashSet (); } public int EventId { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public int VenueId { get; set; } public virtual ICollection Competitors { get; set; } public virtual Venue Venue { get; set; } } public partial class Venue { public Venue() { this.Events = new HashSet (); } public int VenueId { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public virtual ICollection Events { get; set; } } public partial class EFRecipesEntities : DbContext { public EFRecipesEntities() : base("name=EFRecipesEntities") { this.Configuration.LazyLoadingEnabled = false; } protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder) { throw new UnintentionalCodeFirstException(); } public DbSet Competitors { get; set; } public DbSet Events { get; set; } public DbSet Venues { get; set; } } 代码清单8-4的输出如下:
Venue: City Center Hall Event: All Star Boxing --- Competitors ---Big Joe Green Terminator TimVenue: Sports and Recreational Grounds Event: Inter-school Soccer --- Competitors ---St. Mary's School City School
原理
当为我们的模型使用实体框架生成的代码时,我们使用上下文对象中的Include()方法,查询并加载关联实体,这些关联实体可能是实体的列表,可能是一个单独的实体对象 。实体框架中一共有三种不同的方法来加载或查询关联实体: Eager Loading(预先加载), Lazy Loading(延迟加载)和Explicit Loading(显式加载)。示例中我们使用Include()方法演示预先加载关联实体。默认状态下,实体框架是开启延迟加载的,但是在这里,我们把它禁用了。为了使用POCO显式加载导航属性,需要使用DbContext中的Include()方法。
8-3 使用POCO延迟加载
问题
你想使用POCO延迟加载关联实体。
解决方案
假设你有如图8-4所示的模型。
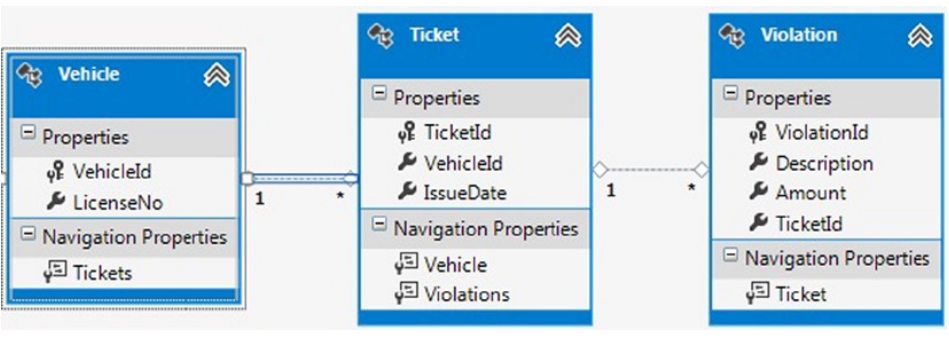
图8-4. 一个关于交通罚单、违规车辆和违规细节的模型
启用延迟加载 ,你不需要做任何事。它是实体框架的默认行为 。代码清单8-5对此进行了演示。
代码清单8-5. 实体类生成,属性设置为Virtual,这是实体框架的默认行为
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { RunExample(); } static void RunExample() { using (var context = new EFRecipesEntities()) { var vh1 = new Vehicle { LicenseNo = "BR-549" }; var t1 = new Ticket { IssueDate = DateTime.Parse("06/10/13") }; var v1 = new Violation { Description = "20 MPH over the speed limit", Amount = 125M }; var v2 = new Violation { Description = "Broken tail light", Amount = 50M }; t1.Violations.Add(v1); t1.Violations.Add(v2); t1.Vehicle = vh1; context.Tickets.Add(t1); var vh2 = new Vehicle { LicenseNo = "XJY-902" }; var t2 = new Ticket { IssueDate = DateTime.Parse("06/12/13") }; var v3 = new Violation { Description = "Parking in a no parking zone", Amount = 35M }; t2.Violations.Add(v3); t2.Vehicle = vh2; context.Tickets.Add(t2); context.SaveChanges(); } using (var context = new EFRecipesEntities()) { foreach (var ticket in context.Tickets) { Console.WriteLine(" Ticket: {0}, Total Cost: {1}", ticket.TicketId.ToString(), ticket.Violations.Sum(v => v.Amount).ToString("C")); foreach (var violation in ticket.Violations) { Console.WriteLine("\t{0}", violation.Description); } } } Console.WriteLine("Enter input:"); string line = Console.ReadLine(); if (line == "exit") { return; }; } } public partial class Ticket { public Ticket() { this.Violations = new HashSet (); } public int TicketId { get; set; } public int VehicleId { get; set; } public System.DateTime IssueDate { get; set; } public virtual Vehicle Vehicle { get; set; } public virtual ICollection Violations { get; set; } } public partial class Vehicle { public Vehicle() { this.Tickets = new HashSet (); } public int VehicleId { get; set; } public string LicenseNo { get; set; } public virtual ICollection Tickets { get; set; } } public partial class Violation { public int ViolationId { get; set; } public string Description { get; set; } public decimal Amount { get; set; } public int TicketId { get; set; } public virtual Ticket Ticket { get; set; } } public partial class EFRecipesEntities : DbContext { public EFRecipesEntities() : base("name=EFRecipesEntities") { } protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder) { throw new UnintentionalCodeFirstException(); } public DbSet Tickets { get; set; } public DbSet Vehicles { get; set; } public DbSet Violations { get; set; } } 代码清单8-5的输出如下:
Ticket: 1, Total Cost: $175.00 20 MPH over the speed limit Broken tail lightTicket: 2, Total Cost: $35.00 Parking in a no parking zone
原理
当生成一个实体数据模型时,延迟加载被默认设置。导航属性默认也被标记为virtual。使用延迟加载,你不需要显式地做任何事。
在上面的控制台程序中,我们没有编写别的代码来加载Violation对象,它是Ticket对象的关联对象。当你在代码中访问关联实体时,延迟加载就生效了。它不需要上下文对象在第一次加载主实体时就加载关联实体,不需要像上一节中使用Include()方法显式加载关联实体。
实体框架交流QQ群: 458326058,欢迎有兴趣的朋友加入一起交流
谢谢大家的持续关注,我的博客地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/VolcanoCloud/